Backend Development and Release Process
Environments
-
Development Environment
- Used for active feature development and initial testing.
-
Staging Environment
- Used for QA, UAT, and pre-production validation.
-
Live (Production) Environment
- Final environment exposed to end users.
Branching Strategy
- Feature Branches → Created from the master-live branch for each new feature or bug fix.
- Development Branch (dev) → Consolidates all feature branches for integration testing before moving to staging.
- Staging Branch → Serves as a pre-release validation branch before moving changes to Live.
- Live Branch → Mirrors the production environment.
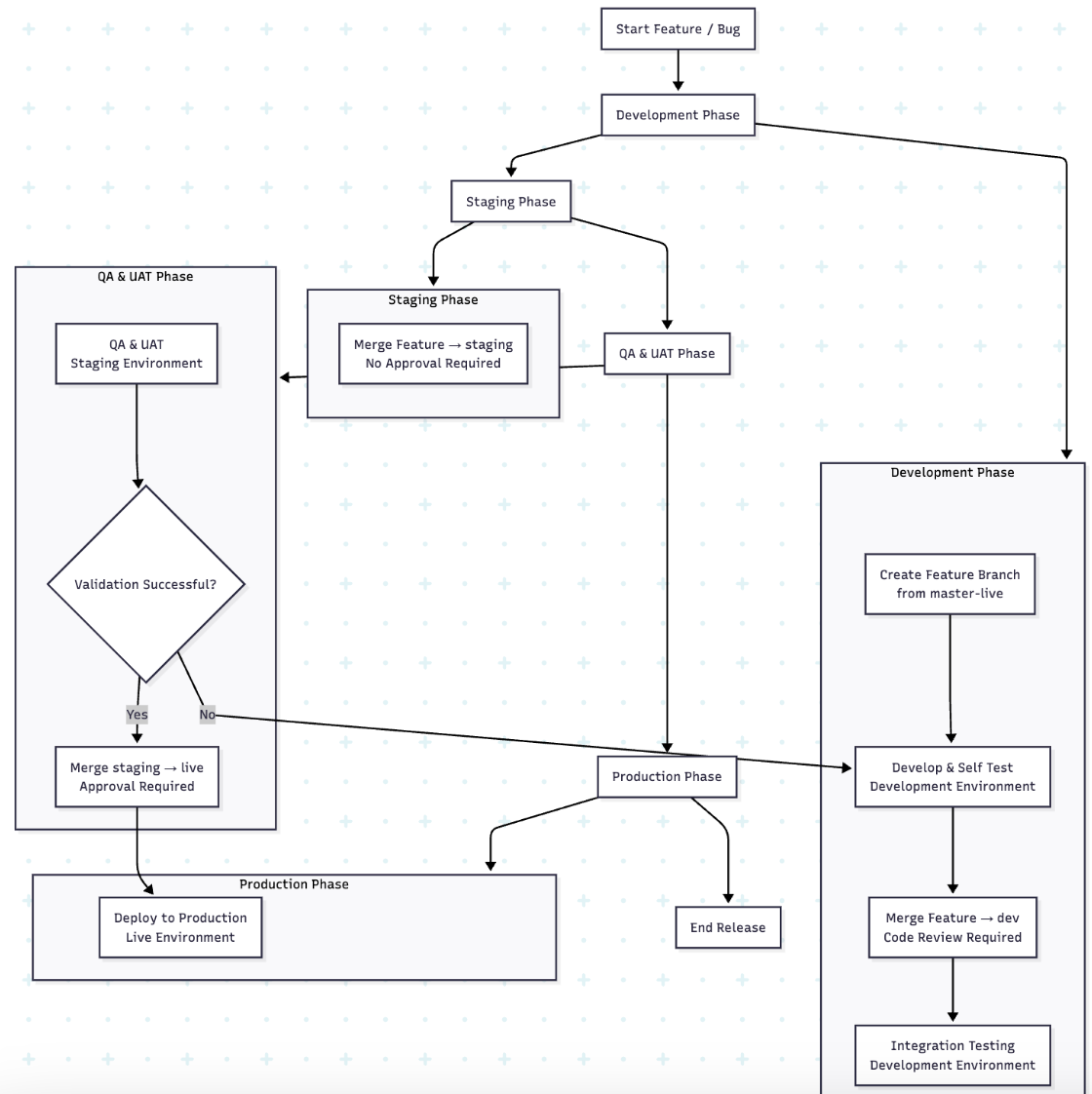
Workflow
-
Feature Development
- Create a feature branch from the master-live branch.
- Complete development and self-test.
-
Development Integration
- Merge the feature branch into the dev branch.
- Code review required for dev merges.
- Perform integration testing in the development environment.
-
Staging Preparation
- Once validated, merge the feature branch into the staging branch.
- Approval not required.
- Deploy to the staging environment for QA and UAT.
-
Production Release
- After successful staging validation, merge the staging branch into the live branch.
Approval required (release owner/lead sign-off). - Deploy to live environment.
- After successful staging validation, merge the staging branch into the live branch.
Release Policy
-
Regular Release Day: Wednesday.
-
Emergency Releases: Allowed outside the regular schedule, but only for urgent fixes with proper approvals.
Git Branching & Release SOP-Mobile Development
Purpose
This SOP defines the standard Git workflow for task-based development, feature stabilization, QA validation, production release, and long-term version tracking.
Branch Strategy Overview
Core Branches
- master → Stable long-term reference branch
- production → Live production code
Supporting Branches
- feature branches → Feature-level integration and QA
- task / developer branches → Individual task or developer work
- release branches → Versioned production snapshots
Workflow Steps
1. Feature Branch Creation
- For each new feature, create a feature branch from
master:
feature/feature-name
- This branch serves as the main integration and QA branch for the feature.
2. Task / Developer Branch Creation
- Each developer creates a task-oriented or developer-specific branch from the feature branch:
task/feature-name/task-name
- All development must be done in these branches only.
3. Merge Task Branch into Feature Branch
- Once a task is completed:
task/* → feature/feature-name
- Pull Request (PR) and code review are mandatory.
- The feature branch should always remain buildable and stable.
4. QA on Feature Branch
- QA testing is performed directly on the stable feature branch.
- QA builds are generated from:
feature/feature-name
- Any QA feedback or bugs:
- Are fixed in task branches
- Merged back into the feature branch
- This cycle continues until QA approval.
5. Release Branch Creation (After QA Approval)
- Once QA approves the feature branch:
release/vX.Y.Z
- The release branch is created from the approved feature branch.
- This branch represents the exact code intended for production.
- No new development is allowed on release branches.
6. Production Deployment
- Production build is generated from the release branch.
- After successful deployment:
release/vX.Y.Z → production
7. Post-Release Feedback & Fixes
- Any production issues or feedback:
- Are addressed via new task branches
- Follow the same flow:
task → feature → release → production
8. Merge to Master
- After the release is stable and verified in production:
production → master
- Ensures
masteralways contains production-proven, stable code.
Rules & Best Practices
- No direct commits to
masterorproduction - No direct commits to feature branches
- QA must be completed on the feature branch
- Every production deployment must have a release branch
- Release branches are immutable (except hotfixes if required)
- Clear commit messages and PR reviews are mandatory
Benefits of This Workflow
- Simpler branching model (no QA branch)
- Clear ownership of feature stability
- Easy rollback using release branches
- Strong traceability from task → feature → production
Release Policy - Mobile
Before releasing any feature, all required approvals must be obtained. Each feature will first be rolled out to 10% of users as an initial release. After collecting and reviewing field feedback and ensuring stability, the feature will then be gradually rolled out to 100% of the application users.